Any new technology can indeed provide us certain ease of use in the application to our dental practice, however, this can only be achieved if we study and learn first how to go about it. Knowing the terms in CBCT can provide us the basics, so, while we are learning its potential for use in our diagnostic and treatment planning half of the battle is done. In continuation, here are the common used terms from P to Z. Please feel free to comment and add terms you may know, so, I can include it here.
P
Panning
Moving the image on-screen side to side, or up and down to see different sections of the whole image.
R
Ray Sum
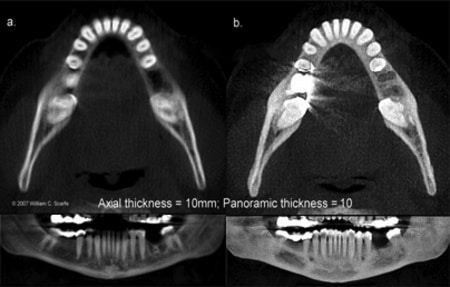
The thickness value of an image created by adding the absorption values of adjacent voxels. You can select the precise thickness desired for a panoramic or cross-sectional view.
Real Size Print
A tick mark that enables you to print with 100% original scale.

Reconstruction
The process by which a software program builds or stacks individual axial CT slices to build a volume. The software then cuts through slices through the volume in a different plane.

ROI
Region of Interest. The selection of necessary parts of slices to reduce the amount of loaded data, increasing operating speed and memory available.
S
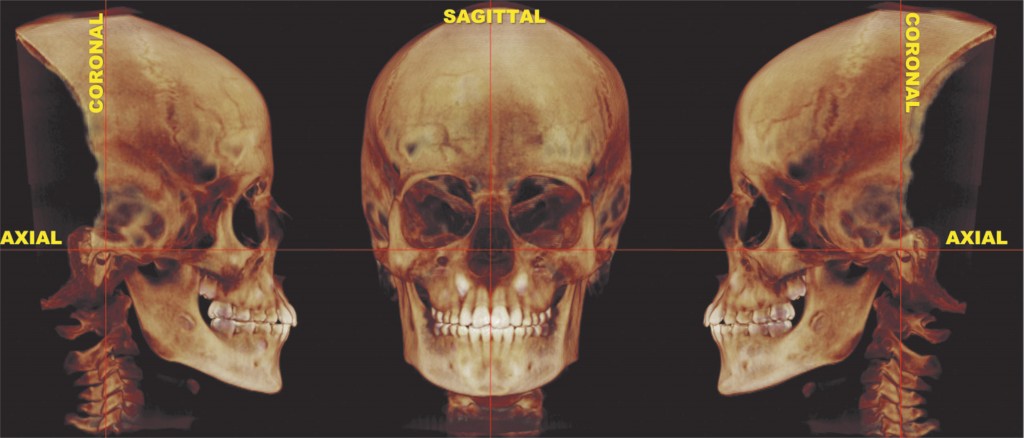
Sagittal Plane
Divides the body into left and right portions.
Scatter
The deflection of radiation from its original path as a result of interaction or collision with media between the source of radiation and an observation point some distance away. Radiation may be received from many directions instead of only from the direction of the source.

Slice
Includes a variety of views for a section of the total image that you select.
SSRO
Sagittal Split Ramus Osteotomy.
A bony cut, performed with saws, burs, chisels, or osteotomes, of the ramus. It is the most common technique used for mandibular advancement.
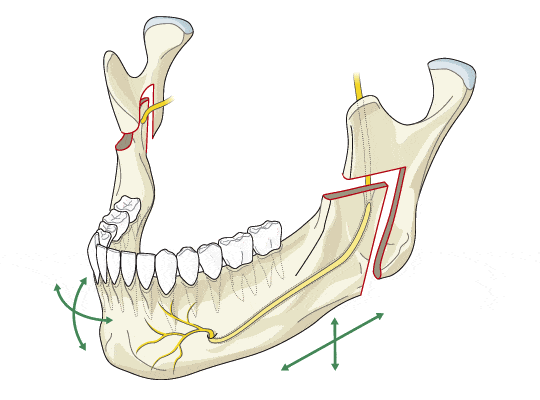
Bilateral sagittal split osteotomies split are used to correct the mandibular deformity except when the surgical movement results in significant lengthening of the ramus or when a sagittal split osteotomy is challenging due to previous surgery. In such cases an Inverted L osteotomy with or without an interpositional bone graft is indicated. Any residual fixation material from previous operations has to be removed. It is unusual for the mandibular ramus to require lengthening on the non-affected side. Therefore it is almost always possible to carry out a sagittal split osteotomy on that side. Although an inverted L-osteotomy can be carried out intraorally, an external approach is often utilized to allow for the placement and fixation of the bone graft.
STP
Standard Temperature and Pressure. A standard set of conditions for experimental measurements to enable comparisons to be made between sets of data.
T
Tomography
A two-dimensional image representing a slice or section through a three-dimensional object.
Imaging by sections or sectioning and in most cases most cases based on the mathematical procedure called tomographic reconstruction.
Transaxials
Denotes the spatial orientation of the imaging plane relative to the patient. The standard orientations are:
Transversal, also called transverse or transaxial, which is perpendicular to the patients' long body axis.
Coronal, also called frontal, which is parallel to the patient's long body axis and left to right. Sagittal, which is parallel to the patient's long body axis and anterioposterior, or front to back.
Other orientations include single or double angle oblique, denoting that the imaging orientation is angulated relative to the standard orientations in one or two directions.
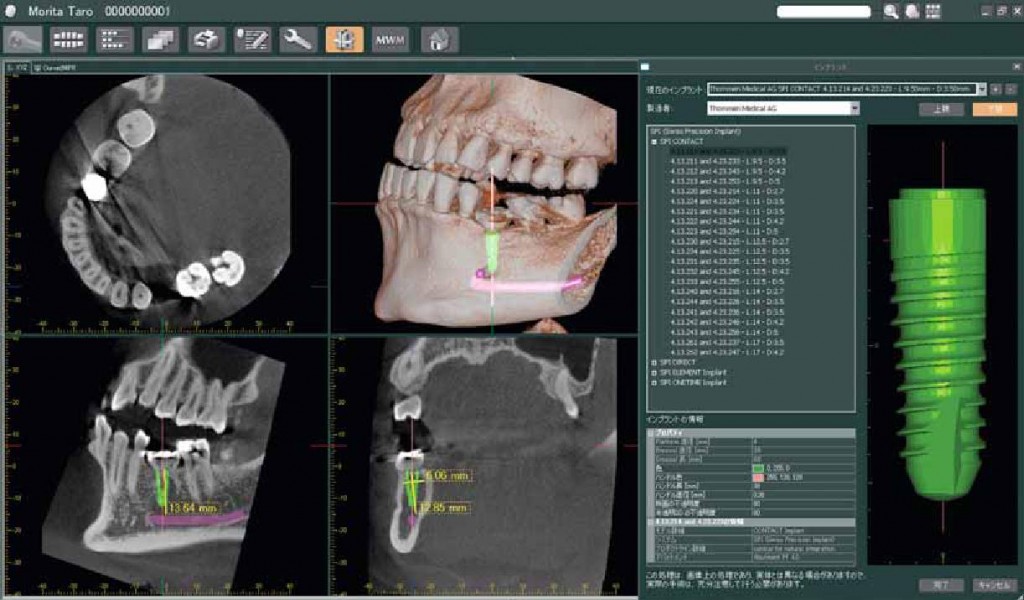
For the picture: Four 3-D screen shots offer an excellent way to see the position and relations of the impacted canines and to plan orthodontic movement. The transaxial (vertical) slices show canine-driven root resorption on the distal and lingual side of the middle portion of the left lateral incisor.
V
Volume Rendering
A technique used to display a 2D projection of a 3D discretely sampled data set. A typical 3D data set is a group of 2D slice images acquired by a CT or MRI scanner. The slices are generally acquired in a regular pattern (e.g. one slice every millimeter) and usually have a regular number of image pixels in a regular pattern.

Voxel
Volumetric Pixel. A volume element, representing a value on a regular grid in 3D space. This is analogous to a pixel, which represents 2D image data. Voxels are frequently used in the visualization and analysis of medical and scientific data. Some true 3D displays use voxels to describe their resolution. For example, a display might be able to show 512×512×512 voxels.
As with pixels, voxels typically do not contain their position in space (their coordinates), but rather, it is inferred based on their position relative to other voxels (i.e. their position in the data structure that makes up a single volume image).
X
X-Ray Tube
A vacuum tube in an x-ray machine designed to produce x-ray photons on demand.
[dvk_social_sharing] [et_bloom_inline optin_id="optin_1"]