Learning the Terms In CBCT Part 3 – From K to O
In continuation, so, we will know the basic terms in CBCT or 3D imaging, here are the common used terms from K to O. Please feel free to comment and add terms you may know, so, I can include it here.
L
LOD Level of Detail.
Activating this feature changes the shape of the 3D model slowly, still providing precise detail.
M
mA
Milliampere. A unit of electric current equal to one thousandth of an ampere. 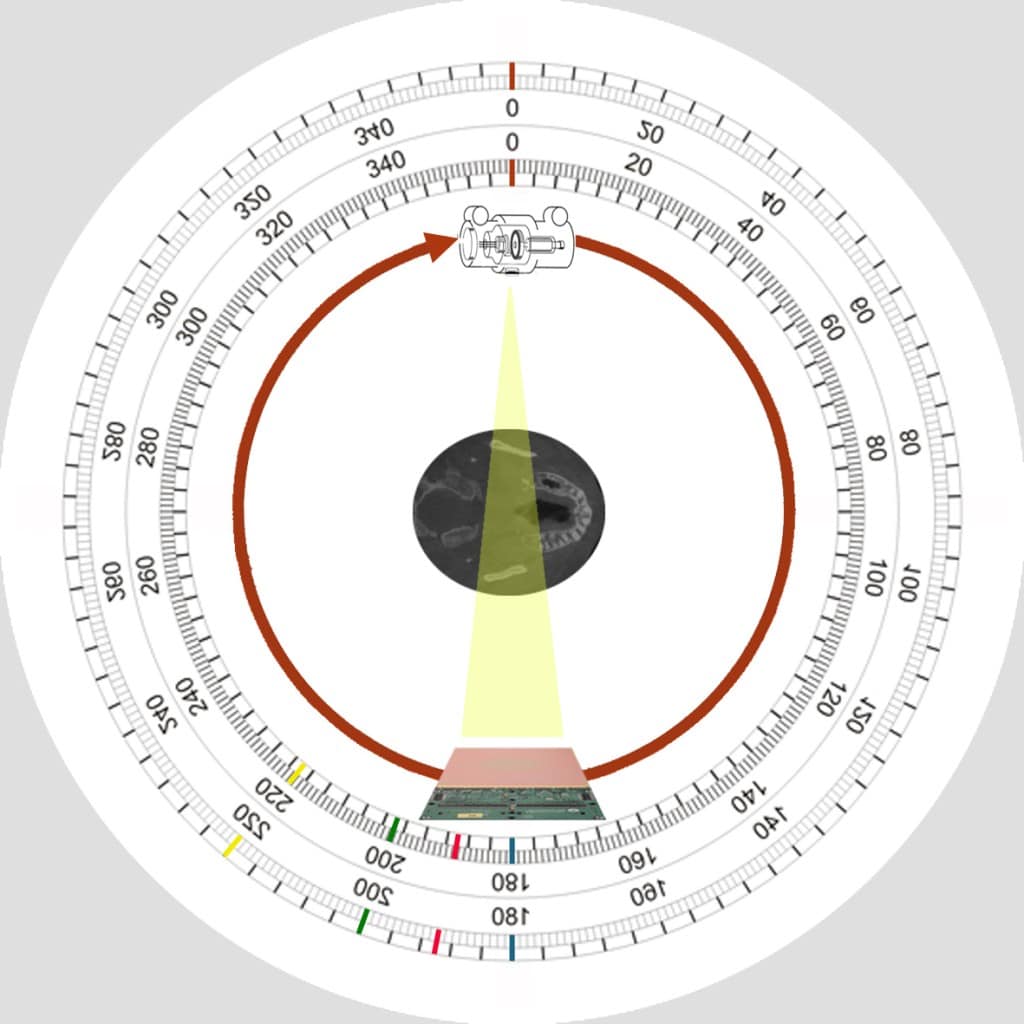
Mandibular Foramen
An opening on the internal surface of the ramus through which divisions of mandibular vessels and nerves pass. Classification of the location of the mandibular foramen and the tip of lingula according to the position of the deepest point of the coronoid notch.

Type 1: Below the mandibular foramen.
Type 2: Coincide with the lowest border of the mandibular foramen.
Type 3: Between the lowest border of the mandibular foramen and the tip of the lingula.
Type 4: Coincide with the tip of the lingula.
Type 5: Above the tip of the lingula.
Mandibular Nerve
The third and most inferior division of the trigeminal nerve (a sensory nerve), which innervates the teeth and mandible, the lateral mucosa of the mandible, and the mucosa of the skin of the cheek, lower lip and chin.

MAR
Metal artifact reduction. Procedures and steps are taken to reduce metal artifacts taken from CBCT

Measure Length
Tool to measure length. Click two points on the image, between which to measure.
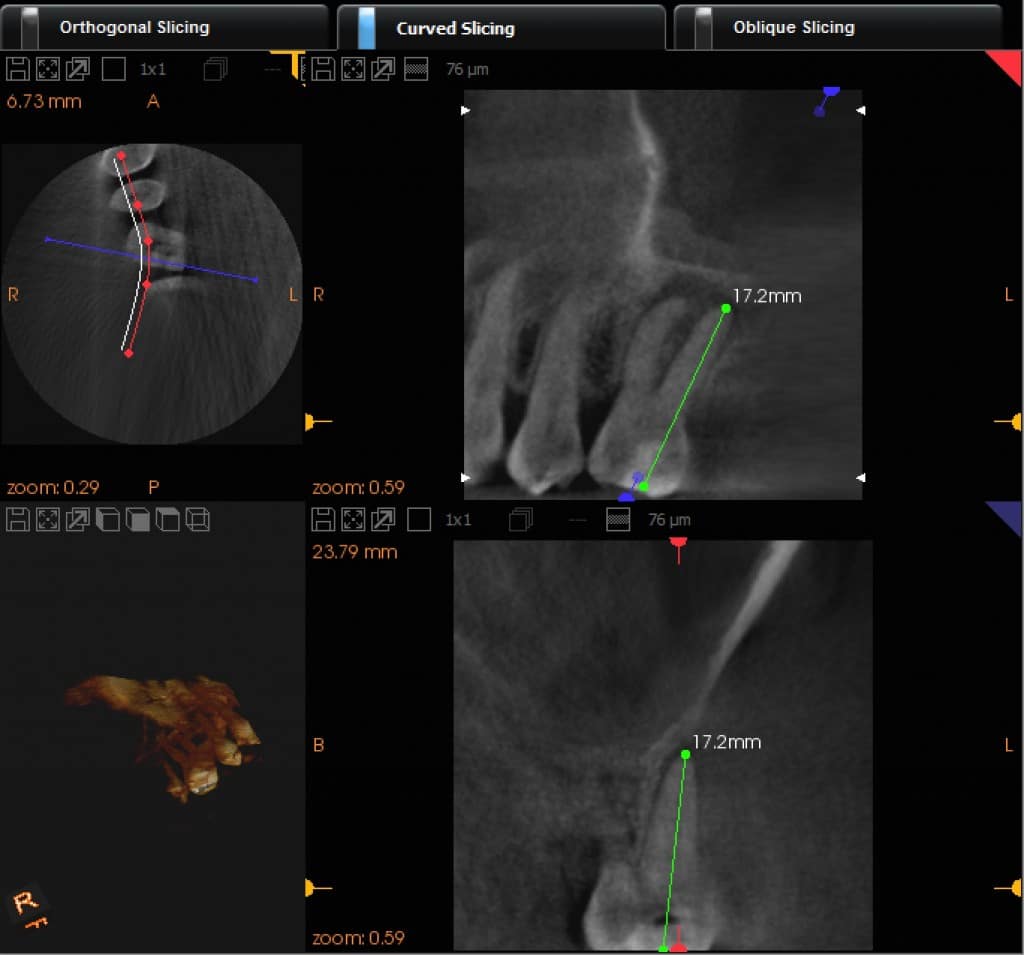
Measure Profile
Tool to profile the bone density of the space between two selected points.
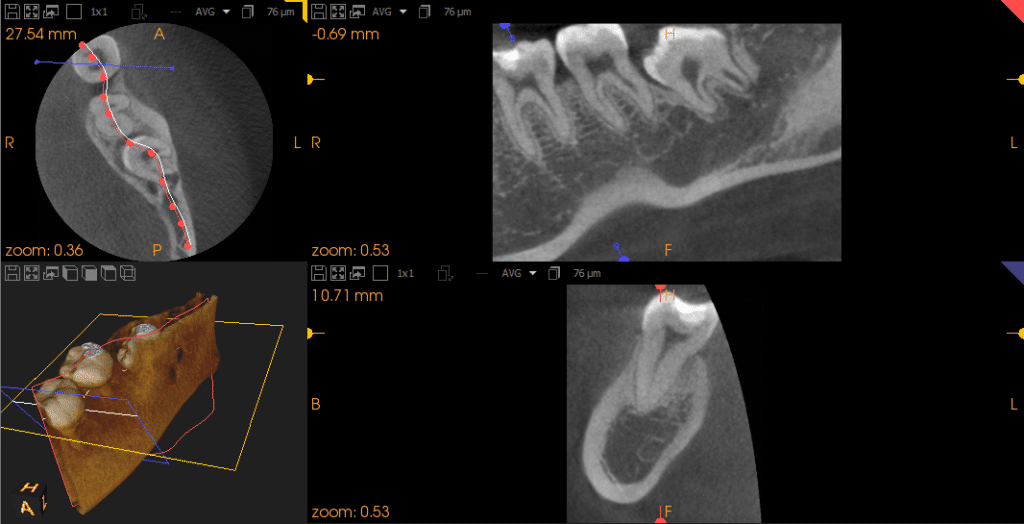
MIP
Maximum Intensity Projection. A computer visualization method for 3D data that projects in a visualization plane the voxels with maximum intensity that fall in the way of parallel rays traced from the viewpoint to the plane of projection. This implies that two MIP renderings from opposite viewpoints are symmetrical images. mIP Minimum Intensity Projection. A computer visualization method for 3D data that projects in a visualization plane the voxels with minimum intensity that fall in the way of parallel rays traced from the viewpoint to the plane of projection.
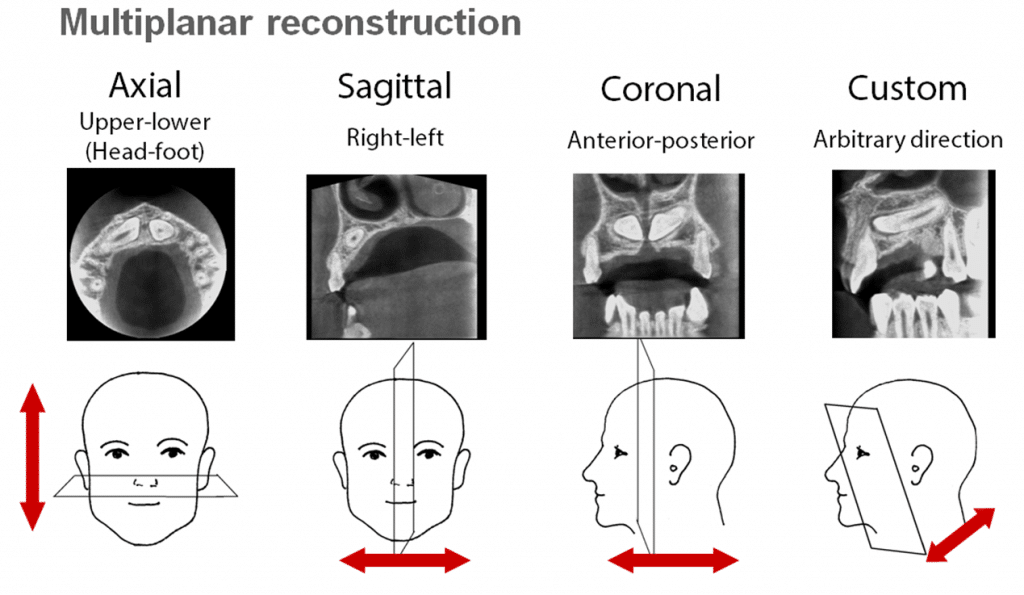
MPR
Multi-Planar Reconstruction.The simplest method of reconstruction. A volume is built by stacking the axial slices. The software then cuts slices through the volume in a different plane. MPRs eliminate superimposition of voxels lying outside the selected plane.
O
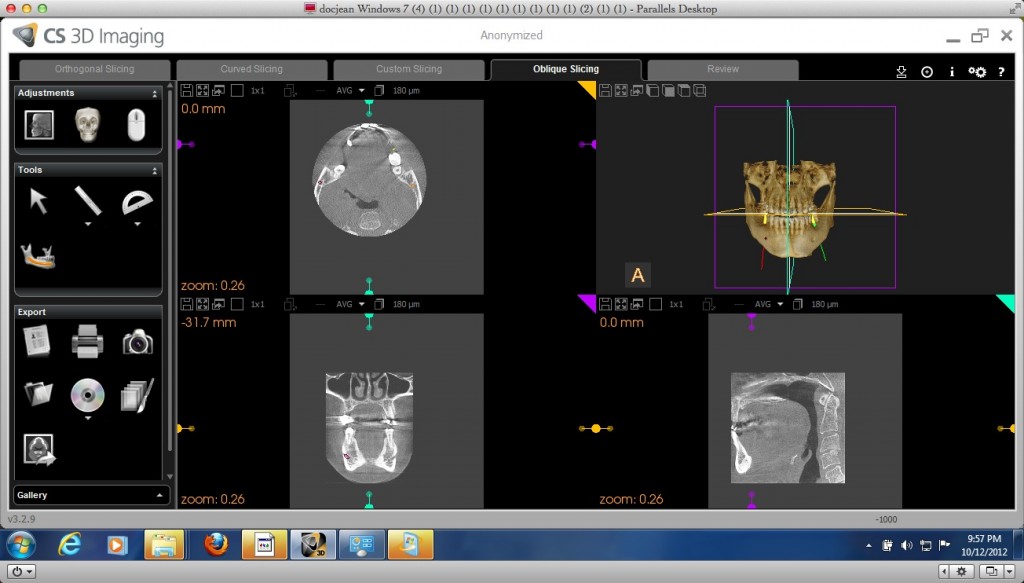
Oblique Slicing
Oblique refers to objects that are neither perpendicular nor parallel to a line or curve. In this view, you can adjust the slice to any oblique angle.
Orthognathic
Surgical procedures designed to correct jaw deformities. Orthognathic procedures are divided into three categories: Maxillary Surgery, Mandibular Surgery, and Bimaxillary Procedures.
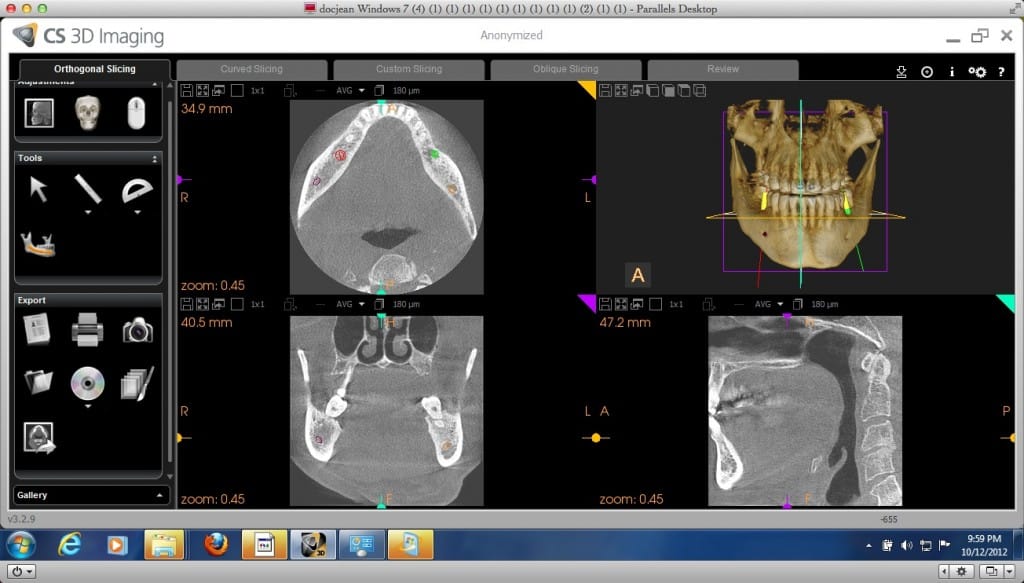
Orthogonal Slicing
Orthogonal relates to right angles. All of the slices (axial, sagittal, coronal) in this view are right angles with each other.
Osteotomy
A surgical operation whereby bone is cut to shorten, lengthen, or change its alignment.
 A. Virtual cast of a patient planned to undergo bi-maxillary osteotomies. B. Creation of virtual osteotomies (Lefort I and bilateral mandibular sagittal osteotomies). C. Virtual reposition of the osteotomized segments to correct the skeletofacial deformity. D. Simulation of the presurgical and (E) postsurgical soft tissue result.
A. Virtual cast of a patient planned to undergo bi-maxillary osteotomies. B. Creation of virtual osteotomies (Lefort I and bilateral mandibular sagittal osteotomies). C. Virtual reposition of the osteotomized segments to correct the skeletofacial deformity. D. Simulation of the presurgical and (E) postsurgical soft tissue result.
[dvk_social_sharing] [et_bloom_inline optin_id="optin_1"]