Learning the Terms In CBCT Part 1- From A to E
Sometimes we find reasons not to try because we are afraid of what we don't know. This shouldn't hinder us because by facing what we don't know and learning about it makes it less daunting, therefore, it opens the door for us to try. CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) is now here and in the next few years it will be the standard digital imaging for certain cases especially in Implantology and Endodontics. So, let's start with something. Let's learn the common words used on CBCT and understanding what it means.
A
ALARA
It is an acronym for "As Low As Reasonably Achievable". This is a radiation safety principle for minimizing radiation doses and releases of radioactive materials by employing all reasonable methods. ALARA is not only a sound safety principle, but is a regulatory requirement for all radiation safety programs.
Anisotropic
It is the property of being dependent on direction. It can also be defined as a difference, when measured along different axes, in a material's physical or mechanical properties such factors in absorbance, refractive index, conductivity, tensile strength, etc. It is totally opposite to isotropic which is used in CBCT.
Artifact (also Artefact)
Misrepresentations of tissue structures seen in medical images. In Dentistry, this commonly occurs when there's metal restorations like Porcelain Jacket Crown fused to Metal.
Attenuation
A general term that refers to any reduction in the strength of a signal, whether by scatter or absorption. Attenuation means penetration. The rate of attenuation (or penetration) is determined by the photon-energy spectrum (KV and filtration) and the type of tissue (fat, muscle, bone) through which the beam passes.
Axial Plane (also Transverse or Horizontal) An X-Y plane, parallel to the ground, which separates the superior from the inferior, or the head from the feet.
B
Beam Hardening
The most commonly encountered artifact in CT scanning. Beam hardening causes the edges of an object to appear brighter than the center, even if the material is the same throughout. The artifact derives its name from its underlying cause: the increase in mean x-ray energy, or "hardening" of the x-ray beam as it passes through the scanned object.
BSSO | Osteotomy | SSRO
Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy. The most commonly used procedure in the treatment of maxillofacial deformities such as prognathism and retrognathism. It is a versatile technique in that it allows movement of the mandible in a posterior direction, but it also allows for relatively large anterior movements.
C
Calibration
The process of determining the relation between the output (or response) of a measuring instrument to the value of the input quantity or attribute, a measurement standard. Calibrations are necessary to establish the characteristics of the x-ray signal as read by the detectors under scanning conditions, and to reduce geometric uncertainties.
 Radiochromic film measurement setups for various CBCT beam widths: (a) axial dose profile measurements with film strips; (b) film calibration with an ion chamber.
Radiochromic film measurement setups for various CBCT beam widths: (a) axial dose profile measurements with film strips; (b) film calibration with an ion chamber.
Capture
Importing the image from the CT Scanner to the computer software.
CAT
Also known as Computerized Axial Tomography. Center Line Used to view the precise center line of a dental implant. Computerized Axial Tomography (also CAT) Tomography in which computer analysis of a series of cross-sectional scans made along a single axis of a bodily structure or tissue is used to construct a three-dimensional image of that structure.
Coronal Plane (also Frontal Plane)
An X-Z plane, perpendicular to the ground, which separates the anterior from the posterior, the front from the back, or the ventral from the dorsal.
CT
Computed Tomography. Originally known as computed axial tomography (CAT scan) and body section roentgenography, CT is a medical imaging method employing tomography where digital geometry processing is used to generate a three-dimensional image of the internals of an object from a large series of two-dimensional x-ray images taken around a single axis of rotation.
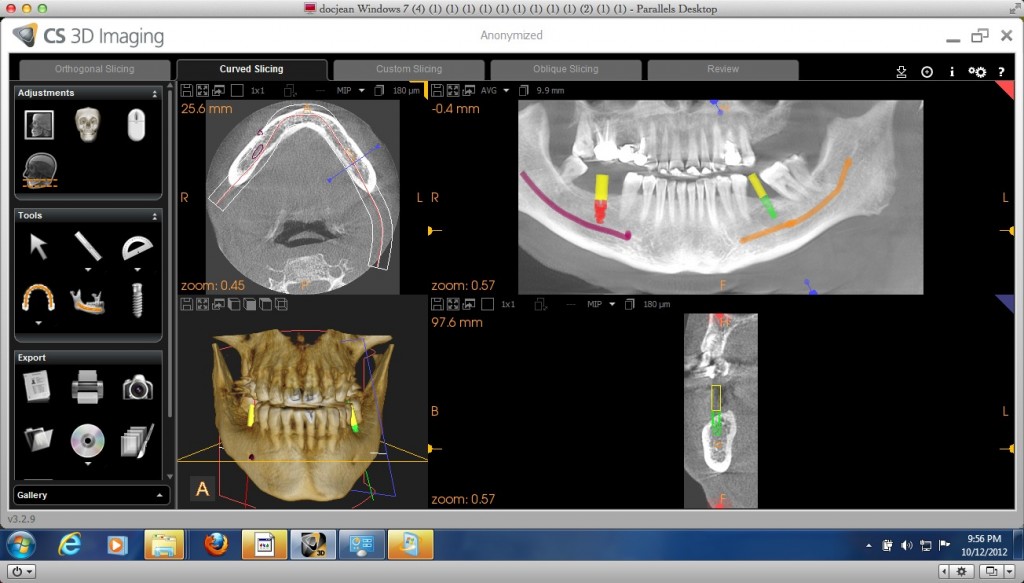
Curved Slicing The slice view in this mode is given along a curved surface (perpendicular to the tangent of the curve at the point selected).
D
Description
Location in which to leave a diagnosis or opinion on the record.
DICOM
Digital Image Communication in Medicine. A standard developed by ACR-NEMA (American College of Radiology National Electrical Manufacturer’s Association) for communications between medical imaging devices.
[dvk_social_sharing] [et_bloom_inline optin_id="optin_1"]